1. Introduction
Computer network security as part of a system that very important to maintain the validity and integrity of the data and to ensure the availability of services for its use.
One of important aspect that is applied is internet banking. Online electronic banking or internet banking systems give everybody the opportunity for easy access to their banking activities. These banking activities may include: retrieving an account balance, money transfers between a user’s accounts, from a user’s account to someone else’s account, retrieving an account history. [1]
Every bank in the world has a different mechanism to provide internet banking services. On this assignment, I will discuss the mechanisms in general, the existing threats and solutions to overcome them by thinking and existing literature.
2. Explanation
2.1. Way of the Internet Banking Works
To use internet banking service, users are required to use a computer or mobile device that has internet access. Generally, all the processes described by the following flowchart:
 Figure 1. Flowchart Internet Banking
Figure 1. Flowchart Internet Banking
 Figure 2. Sketch of Internet Banking Structure
Figure 2. Sketch of Internet Banking Structure
The flowchart of above there is authentication decission process that process where data security is applied. One of the main issues in Iinternet banking related to Internet banking is the weak security in Internet banking application. Therefore it necesary to investigate further the solution to enhance the security issues in Internet banking implementation. In today s high speed world, millions of transactions occur every minute.
In order to ensure the privacy, confidentiality and integrity of the information which are exchanged, disclosed, shared, stored or used on the system and the transactions, the bank engaged the use of a combination of authentication, encryption and auditing mechanisms which serve as powerful barriers against all forms of system penetration and abuse. These mechanisms which are engaged included:
a. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Channel
b. 128-bit Encryption
c. Username & Password protection and authentication
d. Firewalls and
e. Account-locking
All of which have been thoroughly tested in a series to protect and safeguard against known security issues and prevent any form of tampering or theft of information or transactions.
2.2. Internet Banking Security Threats
The most recent banking security threats are listed below:
1. Phishing
Phishing is a scam where fraudsters ‘fish’ for personal details by using hoax emails claiming to be from financial institutions. This method continues to be favored by online thieves.[3]
Hoax emails claiming to be from banks are often generated overseas, and are sent in bulk asking recipient to provide sensitive information such as their username, password, Customer Registration Number or Debit Cards / Credit Cards numbers and PINs by providing a link leading to a fake website, enabling thieves to gather the details for later fraudulent use.
An example of a phishing email is shown below:

 Figure 3. Example of Phising
Figure 3. Example of Phising
2. Spyware and Adware
Spyware is a type of software that secretively collects user information while on the Internet.
Adware is a type of spyware used by marketers to track Internet user’s habits and interests for the purpose of customizing future advertising material. The information is then used to customize future advertisements directed to the user, or can be sold to a third party for the same purpose.
3. Viruses
A computer virus is software that affixes itself to another program like a spreadsheet or word document. While active, the virus attempts to reproduce and attach itself to other programs. This can tie up resources such as disk space and memory, causing problems on any home computer. An email virus is the latest type of computer virus that is transported through email messages and usually replicates by automatically distributing itself out to all contacts on the victims email address book.
4. Trojans
A Trojan is a destructive program that poses as a harmless application. Unlike viruses, Trojans do no replicate themselves and do not need a host program to attach to.
Some Trojans will claim to rid the computer of viruses or other harmful applications, but instead introduce viruses and leave it vulnerable to attacks by hackers and intruders.
5. Keyloggers
If fraudster installs a software called "keylogger" on the computer or the device on which the customer is accessing Online Banking, the software copies to a file , every keystroke typed on that pc. This sensitive information gets captured that the fraudster can later use for fraudulent purposes and illegitimate access to your account.
6. Internet Banking Fraud
Most online banking fraud schemes involve two steps. First, the criminal obtains the customer's account access data, i.e. logon name and password. Second, the criminal uses this information to transfer money to other accounts and withdrawals the funds. For the first step, criminals have employed different schemes in the past.
7. Server Security Threats
It is easy to get a server. Anyone can setup a machine in his basement and start publishing websites like Brute Force Attack, Open Relay, Botnet, DoS, Cross-site Scripting, SQL Injection, Malware, Unpatched Software, and Careless Users. [4]
2.3. Avoid, Prevention and Recovery Various of Threat
Actually, the most of bank have instructed to the customers for make usernames, PINs, passwords and preferred security question and answer ( access codes ) will be used to verify the identity of customers. These access codes will act as a key to access, customer relevant account(s), financial information and the banking facilities, products and services offered via the banking system. To ensure the integrity of these access codes, customers are advised to maintain its confidentiality by not sharing it or making it accessible to any other person.
Based on figure 2. There are two participating entities: the user and the bank. When the user has a PC with a network connection, the most common way to communicate with the bank is via a Web browser, hence banking through the World Wide Web [2] or Web banking. The standard protocol for communication between the browser and the bank’s Web server is then used. It is often referred to as https, which is the http protocol on top of a security layer Http is the communication language of the WWW. A bank will mostly require more security functionality than an ordinary browser is able to provide. Historically, due to US export restrictions, this extra security functionality especially included strong cryptography.
 Figure 4. Example of Bank That Have Already Https [5]
Figure 4. Example of Bank That Have Already Https [5]
Here's how to avoid internet banking threats, particularly for users:
1. Phising.
 Figure 5. Sketch of Avoid Phising
Figure 5. Sketch of Avoid Phising
2. Spyware, adware, virus, trojan and so on
 Figure 6. Sketch of Avoid Spyware, Virus, Trojan, and So On.
Figure 6. Sketch of Avoid Spyware, Virus, Trojan, and So On.
3. Keyloggers
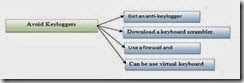 Figure 7. Sketch of Avoid Keyloggers
Figure 7. Sketch of Avoid Keyloggers
4. Avoid Internet Banking Fraud
 Figure 9. Scetse for Defense of Internet Banking Server Security Threats
Figure 9. Scetse for Defense of Internet Banking Server Security Threats
6. Recovery
Actually, prevention is better than recovery, because any computer expert will not be easy to fix infected computer firus and other victims of cyber crime. If it happens is by restoring data that has been backed up. For customers who are infected with the virus and the other victim of cyber crime can contact the bank as soon as possible to deactivate his account. For the case of data theft or hardware and in case of natural disasters, the recovery is to restore data that has been backed up.
3. Summaries
There are many internet banking security threats, like phising, spyware, adware, virus, trojan, keylogger and so on. It is easy to get a server. Anyone can setup a machine in his basement and start publishing websites like Brute Force Attack, Open Relay, Botnet, DoS, Cross-site Scripting, SQL Injection, Malware, Unpatched Software, Careless Users, and so on. For customers who are infected with the virus and the other victim of cyber crime can contact the bank as soon as possible to deactivate his account. For the case of data theft or hardware and in case of natural disasters, the recovery is to restore data that has been backed up. Prevention is better than recovery.
4. References
[1] Claessens, Joris.
On the Security of Today’s Online Electronic Banking Systems.
[2] Tim Berners-Lee and Mark Fischetti. 1999.
Weaving the Web – The Original Design and Ultimate Destiny of the World Wide Web by Its Inventor. HarperCollins Publishers.
[3]
http://www.bankmuscat.com/en-us/Pages/default.aspx
[4]
http://www.webmasterview.com
[5]
https://www.cimbclicks.co.id/

Rahmad Kurniawan
Belum ada tanggapan untuk "INTERNET BANKING SECURITY (MIT Task)"
Post a Comment